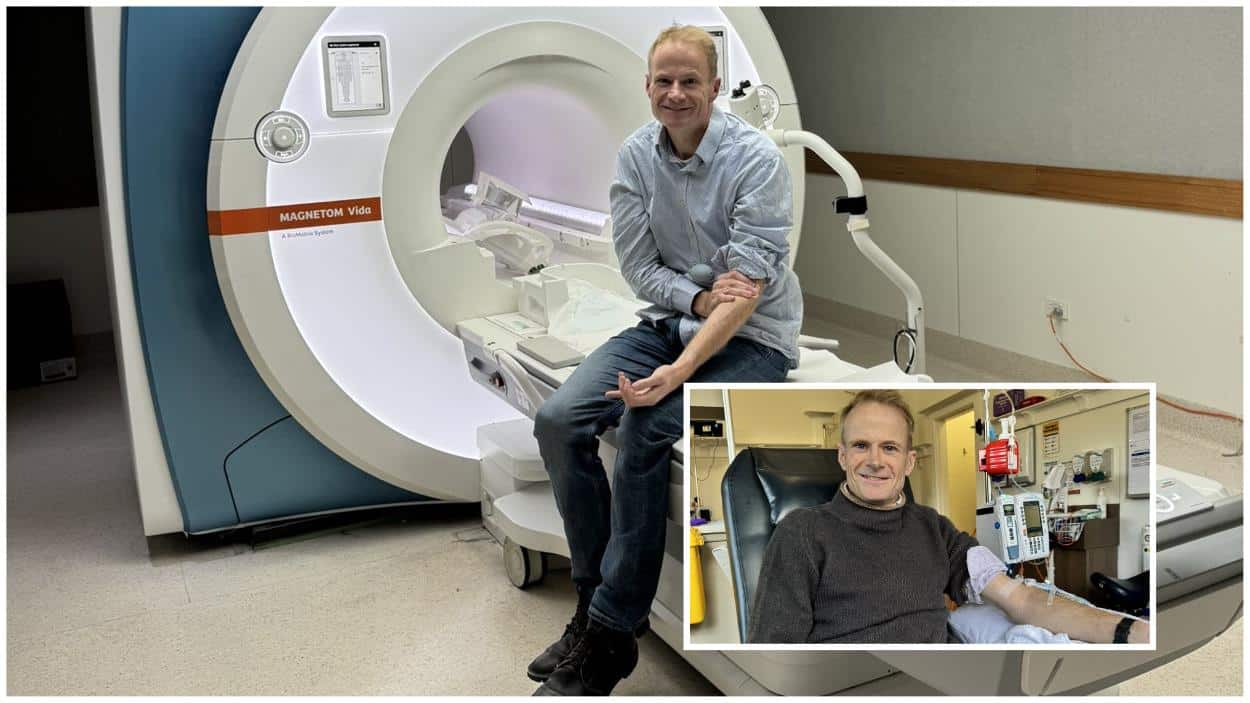
Professor Richard Scolyer, an Australian doctor and a co-director of the Melanoma Institute Australia, celebrated a year free from brain cancer following his groundbreaking treatment.
Diagnosed with glioblastoma, a highly aggressive form of brain cancer, while in Poland last year, Professor Scolyer chose to undergo an experimental therapy he had co-developed. Typically, glioblastoma has a grim prognosis with a median survival rate of about 12 months.
The innovative approach, which aimed to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy, was initially applied to Professor Scolyer, marking him as the first brain cancer patient to undergo this specific pre-surgical treatment regimen. Despite a challenging recovery period marked by seizures, liver complications, and pneumonia, a recent MRI scan showed no signs of the tumour, indicating significant progress and offering him renewed time with his family.
Reflecting on his journey, Professor Scolyer expressed profound relief and joy. “Honestly, I was more nervous than ever before for any scan. I’m just thrilled, I couldn’t be happier. I’m the best I have felt for yonks. It certainly doesn’t mean that my brain cancer is cured, but it’s just nice to know that it hasn’t come back yet, so I’ve still got some more time to enjoy my life with my wife Katie and my three wonderful kids,” he stated.
His colleague, Professor Georgina Long, also a co-director at the Melanoma Institute Australia, emphasized the broader potential of their findings. “We’ve generated a whole heap of data to make a foundation for that next step then so that we can help more people. We’re not there yet. We have to focus on showing that this pre-surgery, combination immunotherapy type of approach works in many people,” she explained.
The pioneering treatment and its initial success have not only provided hope to Professor Scolyer but also stand to potentially transform the approach to treating the approximately 300,000 new cases of brain cancer diagnosed globally each year. The ultimate goal extends beyond prolonging Professor Scolyer’s life; it aims to establish a foundation for more extensive clinical trials. Professor Long noted that while the prospects are promising, significant development time remains before the treatment can be fully approved and widely implemented.
Both professors were honoured with the prestigious Australian of the Year award for their innovative work and profound impact on cancer research.